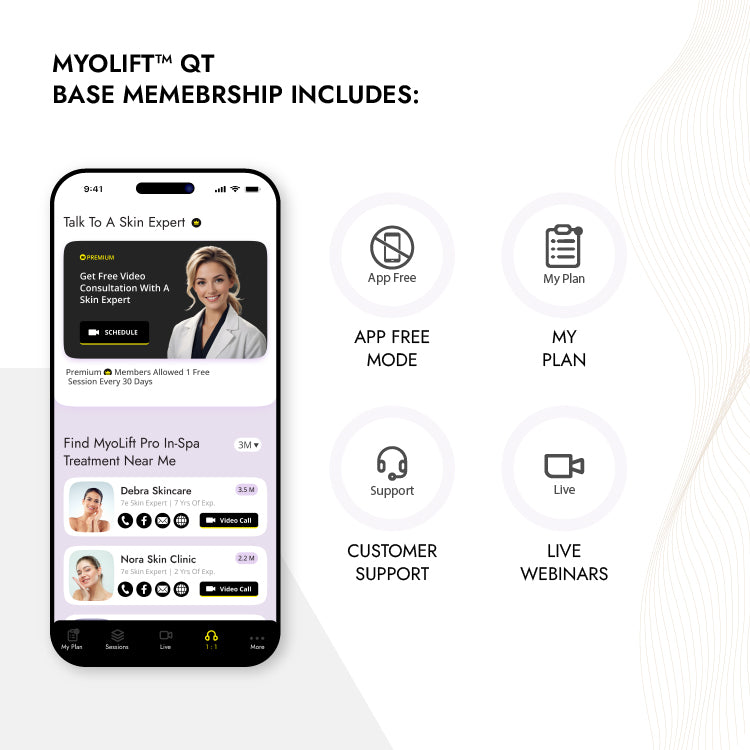
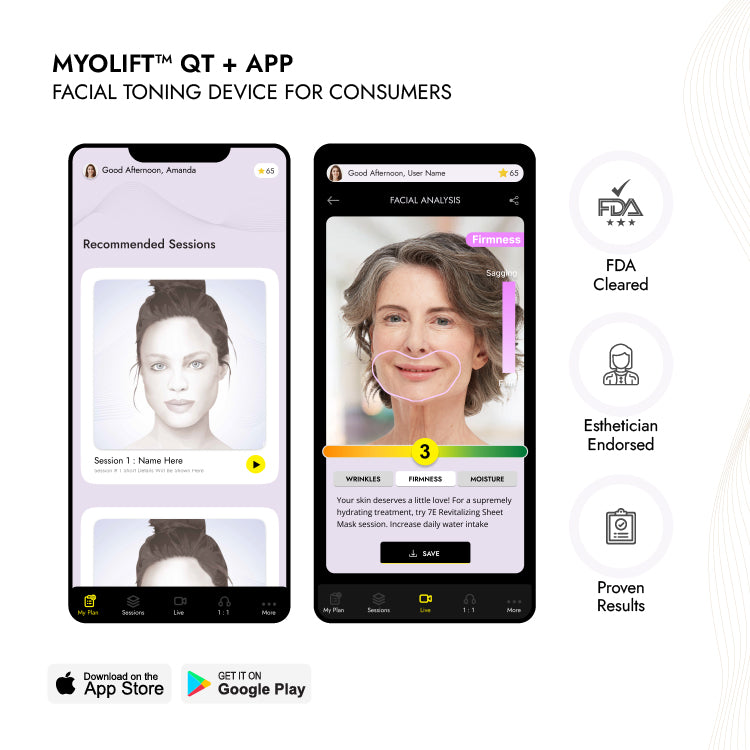
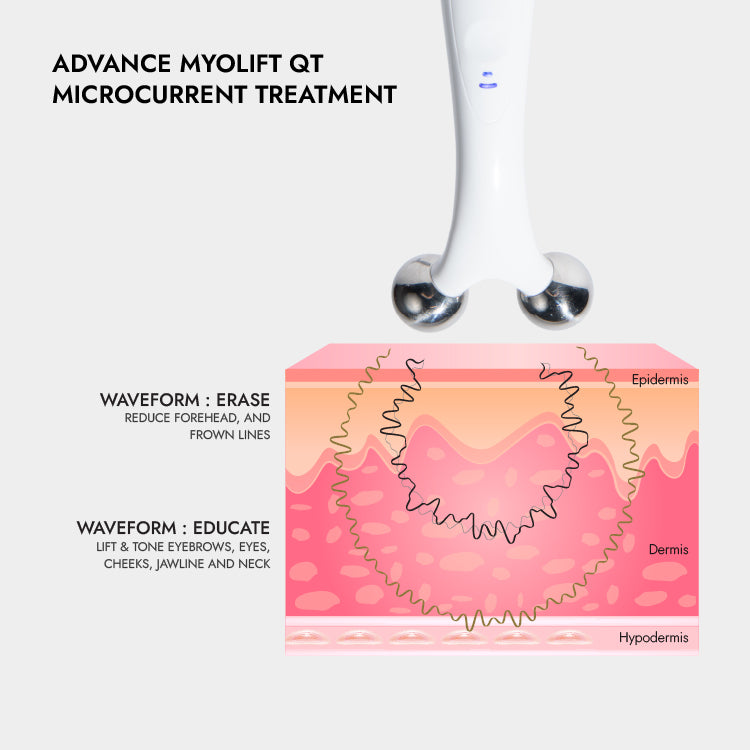
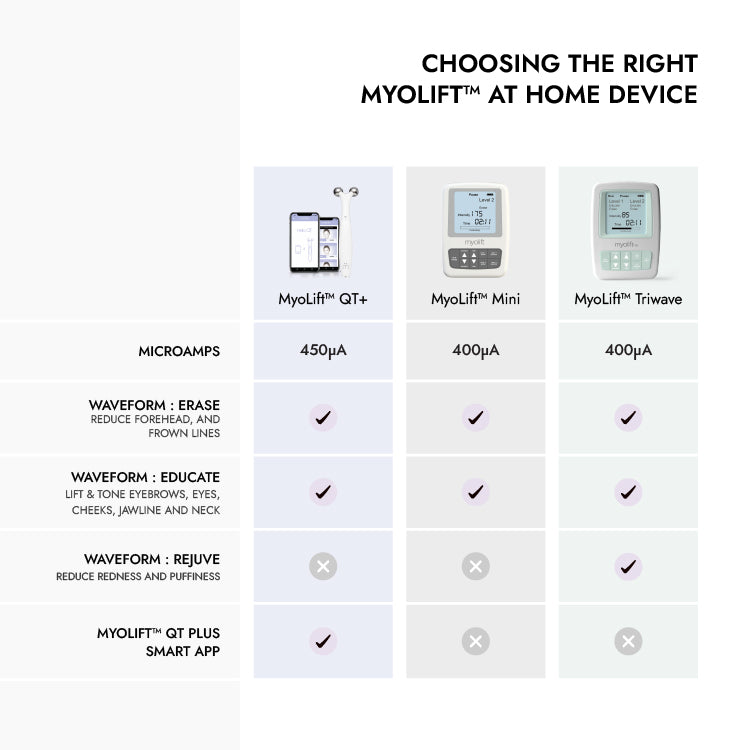
Vitamin C: The Vital Role It Plays To Our Health

Healthy skin readily responds to daily challenges that would otherwise weaken its structure and function. The appearance of our skin reflects our overall internal health and echoes the importance of consuming dietary essentials of macronutrients and micronutrients that work in harmony and contribute to optimum functioning of our skin barrier, skin structures such as collagen and elastin, and daily renewal and repair of all cells throughout the body. Alterations in these nutrients can change the function of these cellular networks that naturally adjust and correct to maintain equilibrium. When the physical and biological skin barriers and structures are encountered with daily environmental over-exposures, including poor lifestyle habits that may have an outcome of nutrient deficiencies, cells cannot optimally perform, repair, or recover from these events. Moreover, these actions begin to manifest through the appearance of the skin in the form of inflammation, dehydration, photo (UV) damage, wrinkling, uneven skin tone and texture with gradual escalation into premature aging and possible disease.
Vitamin C known as L-ascorbic acid is an essential water-soluble micronutrient and functions as a vital cofactor in numerous enzymatic reactions in the human body as well as being an antioxidant in plasma and tissues. Unlike plants and many animals, humans must obtain vitamin C from dietary intake because we do not have the endogenous (internal) ability to manufacture it. It cannot be stored.
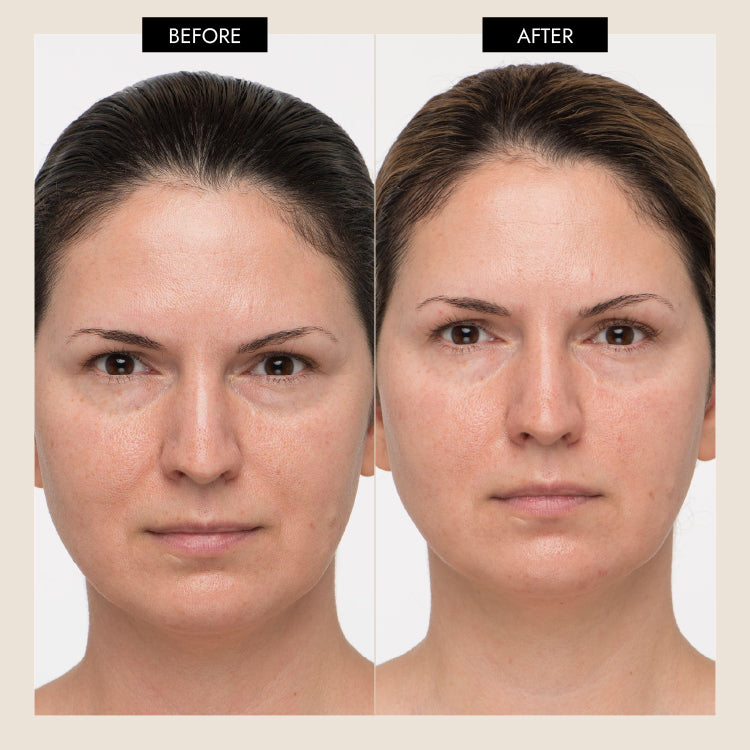
Let’s begin by examining the significant biological benefits of vitamin C, its properties and role within the body, especially regarding its vital relationship to the skin layers with focus on the epidermis and dermis. These insights will support our understanding of studies regarding the impact of topical vitamin C on the skin. Research has clinically confirmed that skin nutrition may be enhanced through topical application of a vitamin C formulation. There is evidence that consistent application has revealed improvement of skin conditions including hydration, inflammation, fine and coarse wrinkles, and dark spots. Additionally, vitamin C may support the skin from long-term damage from ultraviolet rays.,,
Biological Function of Vitamin C – Ascorbic Acid
The function of Vitamin C protects vital molecules in the body such as proteins, lipids (fats), carbohydrates, nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) from free radical damage and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated during normal cell metabolism, immune cell activity, and exposure to toxins and pollutants. Free radicals are highly toxic, unstable molecules that cause damage to nucleic acids, proteins, and cell membranes.
Vitamin C is a co-factor in enzymatic reactions. It is required for the biosynthesis of collagen, carnitine, and the neurotransmitters serotonin and norepinephrine, and regulation of gene expression.
A Potent Antioxidant: Vitamin C can neutralize and remove oxidants such as found in environmental pollutants and after exposure to UV radiation. Vitamin C is an electron donor meaning that it can sequentially donate two electrons to reactive free radicals reducing their activity. The loss of one electron results in the C becoming oxidized. It is essential that vitamin C remain at optimal levels in the body through dietary intake of fresh fruits and vegetables to avoid deficiency of this nutrient.
Interdependence of Vitamin C and Vitamin E and other antioxidants: Vitamin C is called a replenisher of vitamin E. It is capable of regenerating antioxidant capacity of alpha-tocopherol. It prevents the pro-oxidant activity of Vitamin E by decreasing the activity of alpha-tocopheroxyl radical to alpha-tocopherol, thereby acting as a co-antioxidant, contributing to increased total antioxidant status and reduced oxidative stress. The levels of vitamin E, a liphophilic antioxidant, protects cell membranes against oxidative stress and helps maintain the collagen network. Vitamin E levels in the skin can be depleted after UV exposure.
There is a symbiotic relationship between vitamins A, C, and E that help protect the skin from oxidative stress. Vitamins A and E are dependent upon each other.
Collagen Support: Ascorbic acid plays an essential role in the hydroxylation of collagen that enables each collagen fibril to form a uniform and flexible triple helix configuration in the body’s connective tissue.
Presence of Vitamin C In Epidermis & Dermis
Vitamin C is transported from the bloodstream by transport proteins for ascorbic acid and are found on cells in all layers of the skin. Specifically, the epidermal keratinocytes have a high capacity for vitamin C transport because there is limited vascularization (no blood vessels) in the epidermis. Vitamin C is a normal skin component that is found at high levels in both the dermis and epidermis with the C content in the epidermis higher than the dermis.
A Challenged Environment: Vitamin C Deficiency & Decline in the Skin
A vital role for vitamin C in skin health is the relationship between vitamin C deficiency and the loss of several skin functions. Nutrition is essential, given that macronutrients and micronutrients are imperative for healthy skin and appearance. They are vital for maintaining optimal function during collagen synthesis and keratinocyte differentiation. Many vitamin deficiency diseases may result in significant disorders of the skin. For example, B vitamin deficiency may show a patchy red rash, seborrheic dermatitis and fungal skin and nail infections.
Furthermore, the outermost layers of the epidermis can be a challenged environment for nutrient delivery given that it lacks the blood vessels that normally deliver nutrients to cells. Nutrient delivery is dependent on diffusion from the vascularized dermis which may be limited for the outermost layers of the epidermis. The chemical nature of the stratum corneum shows that there is little movement of extracellular fluid between the cells due to the complex lipid/protein crosslink structure forming the skin barrier.
Dietary Intake: Inadequate intake of vitamin C from 4 to 12 weeks symptomatically presents irritability and anorexia, poor wound healing, gingival swelling and loss of teeth, ecchymosis (bruising), and hyperkeratosis. Other indications include anemia, myalgia, bone pain, easy bruising, swelling, petechiae.
Risk Factors for Vitamin C Deficiency
The Vitamin C story reveals insight into a greater world regarding the influence of all macro and micronutrient molecules upholding the health of the skin.
External application of Vitamin C in an efficacious formulation can be advantageous in skin support. The clinical effect of topical use demonstrates that it can be a powerful antioxidant in the skin that can help protect against photoaging, ultraviolet-induced immunosuppression, and photo carcinogenesis It has been found to slow early skin aging and combats harmful free radicals that encounter the skin from the external environment and even from inside the body as a normal process such as metabolism. Ultimately, topical application of vitamin C may improve the overall appearance of the skin
Introducing 7E Wellness Revital C Serum
The Vitamin C Serum is a powerful nourishing, boosting complex containing protective and supporting components for the skin. The collection of antioxidants, hydrating, and soothing ingredients work synergistically to nourish, protect, and neutralize free radical activity resulting from sun exposure, pollution, and additionally protects and may increase collagen. Apply morning and night.
Functional Ingredients and Benefits:
L-Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) is a potent and refined version of vitamin C that neutralizes free radicals, protecting cells from oxidative damage from sun damage, air pollution and helps brighten the skin and reduce hyperpigmentation
Organic Aloe Barbadensis Leaf Extract (Aloe Vera) is rich in nutrients and antioxidants, and offers anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, humectant properties and soothes the skin.
Hyaluronic Acid is a natural mucopolysaccharide that supports the increase of moisture content in the skin preventing transepidermal water loss. (TEWL). It also supports supple stretch and flex and reduces fine lines and wrinkles.
White Tea Leaf Extract (Camella Sinensis): High in antioxidants, white tea extract contains polyphenols, tannins, and flavonoids. It is rich in natural anti-inflammatory and protective components.
CoQ10 (Ubiquinone) is full of antioxidant properties that protect the skin from environmental stressors and from lipid peroxidation. It supports to reduce wrinkle depth, assists in copper utilization to repair wrinkles. It energizes the skin, supports skin tone, and supports water retention.
Tocopherol Acetate (Vitamin E) is a natural form of stable vitamin E and a potent oil-soluble antioxidant. It also assists in the absorption of vitamin C.